Vision
We aim to turn today’s opaque LLMs into white-box systems whose internal mechanisms are legible and steerable. Evidence suggests that large models exhibit some degree of latent modularity—subnetworks that tend to specialize in perception, mathematics, coding, chain-of-thought, physical priors, and related functions.
By identifying, shaping, and strengthening these modules—and enforcing sparsity so only the right pieces fire—we obtain models that are smaller, faster, and cheaper to run, with transparent, controllable decision pathways and stronger out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization.
Expected Outcomes
We target (a) compute efficiency via activation sparsity and specialist routing; (b) bias isolation/removal, measured by group-fairness and counterfactual-fairness tests; (c) generalization gains on OOD splits and cross-domain tasks; and (d) faithful transparency, measured by decision-trace agreement with interventional ground truth.
Why This Matters
White-box LLMs (and VLMs) make it possible to audit, govern, and tune foundation models for regulated, safety-critical, and creative applications. By isolating causal functions and exposing controllable routes, we deliver models that are more efficient, less biased, easier to trust, and that transfer better across tasks and domains.
Introduction
One of the most important challenges on the path to artificial general intelligence (AGI) is improving the reasoning ability of large language models (LLMs).
While recent long chain-of-thought (long-CoT) systems (e.g., OpenAI-o1, DeepSeek-R1) demonstrate remarkable performance by engaging in deliberate, step-by-step reasoning, they typically rely on expensive reinforcement learning (RL) or supervised fine-tuning (SFT) with large volumes of high-quality data. Such methods are difficult to scale, costly to train, and often unstable.
Contribution
Our research reveals that the long-CoT ability is already present inside base models, but remains dormant. We show that it can be activated efficiently through activation control, without retraining the model from scratch.
Key Empirical Findings
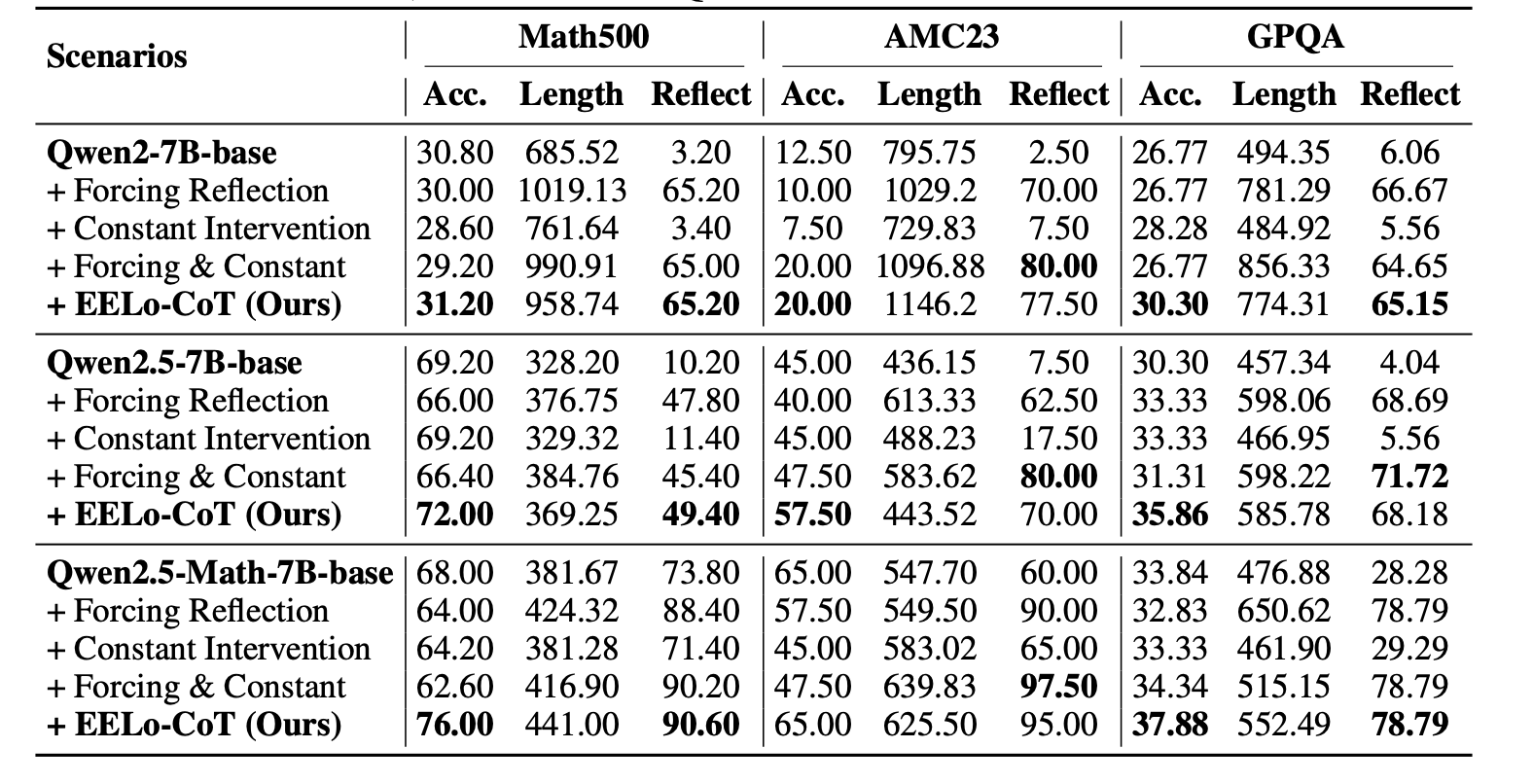
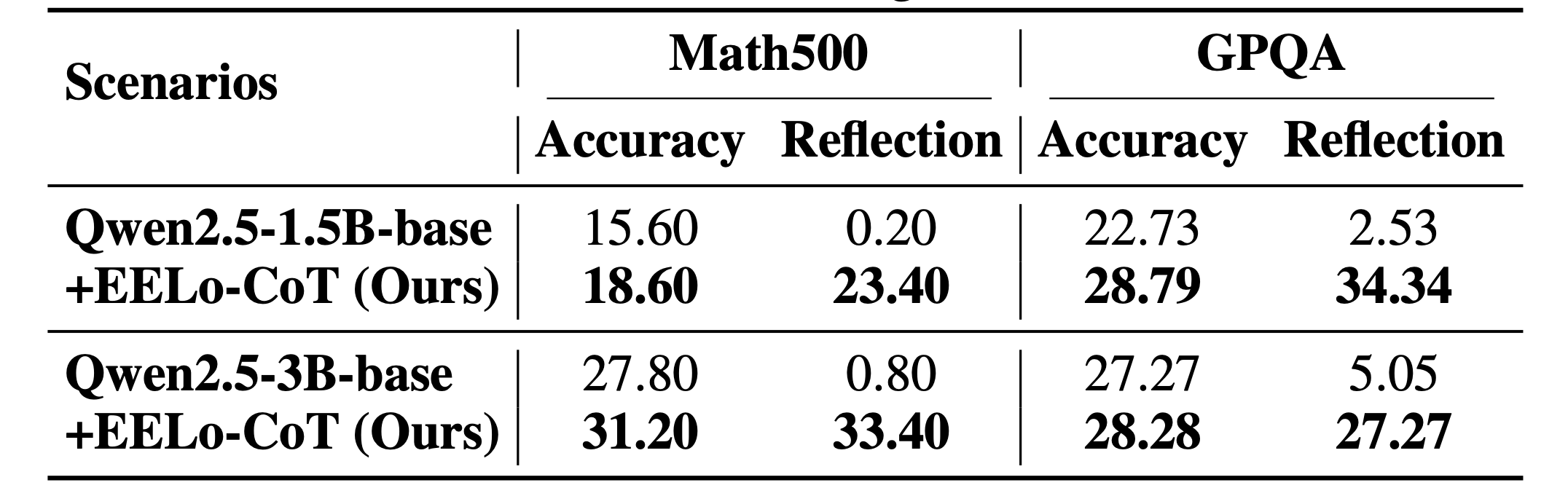
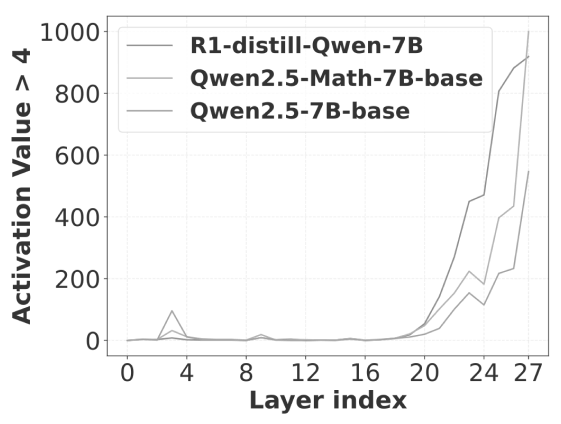
- Long-CoT related activations concentrate in the final layers of the model.
- Their dynamics follow predictable patterns (sharp rise followed by logarithmic decay).
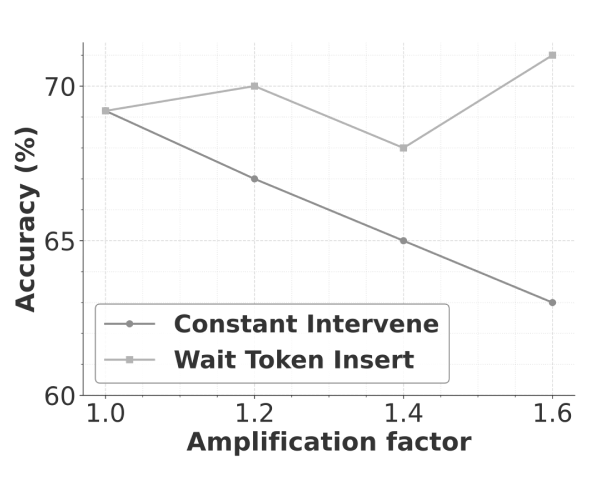
- Simple amplification, combined with reflection triggers (such as a wait token), reliably elicits long-form reasoning.
Reference
Zhao, Zekai, Qi Liu, Kun Zhou, Zihan Liu, Yifei Shao, Zhiting Hu, and Biwei Huang. "Activation Control for Efficiently Eliciting Long Chain-of-thought Ability of Language Models." arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.17697 (2025).
Sparse Activations when processing Long CoT
Smaller
More Efficient Models
Improved
Generalization across Tasks and Domains
Transparent
& Controllable Decision Pathways
Isolation& Removal
of Spurious Biases
linkedin →
X →
© 2025 Abel.AI, Inc. All rights reserved.
Research Benefit
This activation control framework demonstrates a new path for scalable and interpretable reasoning in LLMs:
- Unlocks latent reasoning without costly retraining.
- Provides controllable, transparent mechanisms for eliciting slow, reflective thought.
- Offers parameter-efficient fine-tuning for adapting reasoning to new domains.
This establishes a foundation for causality-aware, intervention-ready intelligence — enabling more reliable AI agents for science, finance, and high-stakes decision-making.
- Our work demonstrates that the long-CoT ability already exists in base LLMs and can be efficiently elicited without costly retraining. By identifying and amplifying key activations, inserting reflective triggers, and employing parameter-efficient adaptation, we elicit deliberate, self-reflective reasoning.
- This approach provides a scalable and generalizable method for building LLMs with improved accuracy, interpretability, and robustness in complex reasoning domains.
White-box LLM / VLM
Identifying and enhancing modularity & sparsity in LLMs - so that different submodules specialize in distinct cognitive or causal functions.
Eliciting Long Chain-of-thought Capability